Vasectomy: Why It Is Done?
A vasectomy is a permanent method of male birth control (male sterilization). Only consider this method when you are sure that you do not want to have a child in the future.
Vasectomy Procedure Overview
A vasectomy prevents the release of sperm when a man ejaculates. During a vasectomy, the vas deferens from each testicle is clamped, cut, or otherwise sealed.
It usually takes several months after a vasectomy for all remaining sperm to be ejaculated or reabsorbed. You must use another method of birth control until you have a semen sample tested and it shows a zero sperm count. Otherwise, you can still get your partner pregnant.
Surgery to reconnect the vas deferens (vasectomy reversal) is available. But the reversal procedure is difficult. You should be certain you’re comfortable with the permanent nature of the procedure before having it done.
Vasectomy Advantages
Vasectomy is a safer procedure that causes fewer complications than tubal ligation in women.
Although vasectomy can be relatively expensive, it is a one-time cost. The cost of other methods, such as birth control pills or condoms and spermicide, are likely to be greater over time.
What Happens During a Vasectomy?
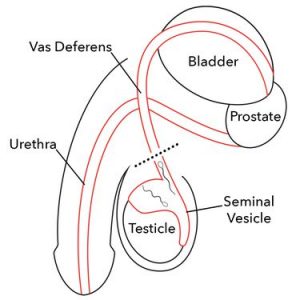 Your testicles and scrotum are cleaned with an antiseptic and possibly shaved.
Your testicles and scrotum are cleaned with an antiseptic and possibly shaved.- You may be given an oral medicine to reduce anxiety.
- Each vas deferens is located.
- A local anesthetic is injected into the area.
- Your doctor makes one small opening in your scrotum. Through an opening, the two vas deferens tubes are cut. The two ends of the vas deferens are tied, stitched, or sealed. Electrocautery may be used to seal the ends with heat. Scar tissue from the surgery helps block the tubes.
- The vas deferens is then replaced inside the scrotum. Stiches are generally not required to close the opening in the scrotum.
The procedure takes about 20 to 30 minutes and can be done in an office or clinic. It may be done by a family medicine doctor, a urologist, or a general surgeon.
Vasectomy Recovery: What to Expect Following the Surgery
Your scrotum will be numb for 8-10 hours after a vasectomy. Apply cold packs to the area and lie on your back as much as possible for the rest of the day. Wearing snug underwear or a jockstrap will help ease discomfort and protect the area.
You may have some swelling and minor pain in your scrotum for several days after the surgery. Unless your work is strenuous, you will be able to return to work in 1 or 2 days. Avoid heavy lifting for a week following surgery.
You can resume sexual intercourse as soon as you are comfortable, usually in about a week, but you can still get your partner pregnant until your sperm count is zero. You must use another method of birth control until you have a follow-up sperm count test 6-8 weeks after the vasectomy. Once your sperm count is zero, no other birth control method is necessary.
A vasectomy will not interfere with your sex drive, ability to have erections, sensation of orgasm, or ability to ejaculate. However, you may have occasional mild aching in your testicles during sexual arousal for a few months after the surgery.
